Salivary Transferrin
In the bloodstream the majority of steroid hormones are bound either to non-specific proteins such as albumin or to specific proteins such as corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG) or sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). These protein molecules are generally too large to diffuse from the blood stream into the saliva glands. Consequently, only the 1-15% of […]
Salivary Total Protein
Total protein is a non-specific measure of the total amount of all proteins present in a solution. It is used to examine changes in overall protein secretion in blood or saliva that are associated with disease states, or to look for differences in the ratio of specific proteins (or other analytes) to total protein that […]
Salivary TNF-Alpha
*Also available as part of the Salimetrics Cytokine Panel* Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-Alpha) is a member of a family of small biologically active proteins known as cytokines. TNF-α plays a key role in the innate inflammatory response in vertebrates. When macrophages and T cells detect an invading pathogen, they produce TNF-α, triggering local […]
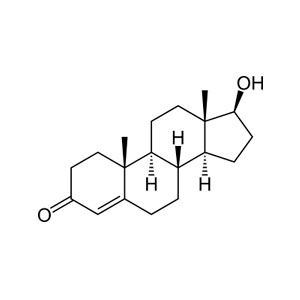
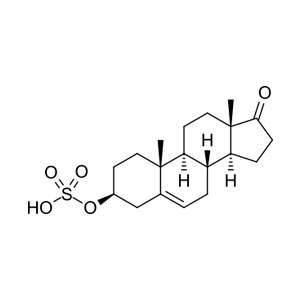
Salivary Testosterone
Testosterone is an anabolic steroid hormone synthesized from androstenedione in the Leydig cells of the testes of males and, in smaller quantities, in the ovaries of females. (1) Small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands in both sexes. In both men and women a large portion of total testosterone production occurs in peripheral tissues by conversion of circulating DHEA-S, DHEA, and androstenedione. […]
Salivary SIgA
Secretory Immunoglobulin A (SIgA) is a subclass of Immunoglobulin A (IgA), an antibody that plays a critical role in mucosal immunity. SIgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions from tear glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, the respiratory system, the genito-urinary tract, and the gastrointestinal tract. (1) SIgA is not synthesized by mucosal epithelial cells in […]
Salivary Progesterone
Progesterone (4-pregenene-3,20-dione) is a steroid hormone of primary importance in ovulation, fertility, pregnancy, and menopause. Synthesis of progesterone takes place in the placenta, adrenal glands, and gonads. (1-4) In normal, non-pregnant women during the mid-luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, progesterone exhibits a prominent circadian rhythm with additional ultradian components. Peak production occurs in the […]
Salivary Melatonin
Analysis of melatonin in saliva effectively enables researchers to design non-invasive studies that assess circadian timing and evaluate the degree of circadian phase abnormalities in association with major diseases, conditions, administration of pharmaceutical compounds, seasonal affective disorder, jet-lag and night shift work, etc., due to a strong correlation with serum melatonin concentrations. It also pertains […]
Salivary Interleukin-6
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is one of a family of biologically active small protein molecules known as cytokines. It is released by a variety of tissues, including activated leukocytes, adipocytes, and endothelial cells, and it is involved in many processes in the body. IL-6 plays an important role in stimulating the immune response to infection or trauma […]
Salivary Interleukin-1 Beta
*Also available as part of the Salimetrics Cytokine Panel* Interleukin-1β (IL-1 beta) is one of a family of biologically active small protein molecules known as cytokines. Cytokines are produced by a number of different cell types, including macrophages, monocytes, fibroblasts, and dendritic cells. (1,2,3) IL-1β is an example of a pro-inflammatory cytokine, since it is involved […]
Salivary Insulin
Insulin, a core anabolic peptide hormone, is responsible for regulating the metabolism of nutrients such as glucose and fatty acids to promote their absorption into fat, liver, and skeletal muscle cells. It also suppresses the breakdown of proteins into amino acids. Circulating insulin levels stimulate cellular glucose oxidation, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and proteogenesis to maintain glucose […]
Salivary Interleukin-8
Interleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as neutrophil chemotactic factor, belongs to the CXC chemokine family and mainly serves as an immune mediator of neutrophil-dependent acute inflammation (2). IL-8 is produced in various cells and tissues such as phagocytes and mesenchymal cells exposed to inflammatory stimulus, and primarily targets the recruitment and activation of neutrophil granulocytes and […]
Salivary Estrone
Estrone (3-hydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17-one; E1) is one of the three main estrogenic steroid hormones produced in humans. Circulating estrone levels are relatively high at birth in both males and females, decrease postnatally, and increase during puberty. (1) Of the three major estrogens, estrone is predominant after menopause in women. (1)
Salivary Estriol
Estriol (1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3,16α,17β-triol; E3) is a female sex steroid hormone largely associated with pregnancy and fetal development. Fetal adrenal DHEA-S is metabolized in the fetal liver to 16α-hydroxy-DHEA-S, which is then converted to estriol in the placenta. (1,2) By the second trimester, about 90% of the estriol produced is derived from this fetal adrenal DHEA-S. (2) […]
Salivary Estradiol
Estradiol is one of the three main estrogenic steroid hormones present in humans. It is the most active naturally secreted estrogen. (1) In menstruating women, estradiol is produced primarily by the ovarian follicles from testosterone, with additional amounts produced by extraglandular conversion of testosterone in peripheral tissues. (1,2,3,4) Concentrations peak mid-cycle, marking ovulation, followed by […]
Salivary DHEA-S
DHEA-S is a steroid hormone produced primarily in the adrenal cortex. It is the sulfated version of the human steroid DHEA, and, like DHEA, it is secreted in response to ACTH. DHEA-S has been reported to have a diurnal rhythm, but the findings have varied, and some studies found no variation. (1) DHEA-S in the blood […]
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)