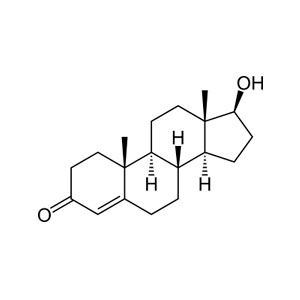
Salivary Testosterone
Testosterone is an anabolic steroid hormone synthesized from androstenedione in the Leydig cells of the testes of males and, in smaller quantities, in the ovaries of females. (1) Small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands in both sexes. In both men and women a large portion of total testosterone production occurs in peripheral tissues by conversion of circulating DHEA-S, DHEA, and androstenedione. […]
Salivary SIgA
Secretory Immunoglobulin A (SIgA) is a subclass of Immunoglobulin A (IgA), an antibody that plays a critical role in mucosal immunity. SIgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions from tear glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, the respiratory system, the genito-urinary tract, and the gastrointestinal tract. (1) SIgA is not synthesized by mucosal epithelial cells in […]
Salivary Progesterone
Progesterone (4-pregenene-3,20-dione) is a steroid hormone of primary importance in ovulation, fertility, pregnancy, and menopause. Synthesis of progesterone takes place in the placenta, adrenal glands, and gonads. (1-4) In normal, non-pregnant women during the mid-luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, progesterone exhibits a prominent circadian rhythm with additional ultradian components. Peak production occurs in the […]
Salivary Melatonin
Analysis of melatonin in saliva effectively enables researchers to design non-invasive studies that assess circadian timing and evaluate the degree of circadian phase abnormalities in association with major diseases, conditions, administration of pharmaceutical compounds, seasonal affective disorder, jet-lag and night shift work, etc., due to a strong correlation with serum melatonin concentrations. It also pertains […]
Salivary Insulin
Insulin, a core anabolic peptide hormone, is responsible for regulating the metabolism of nutrients such as glucose and fatty acids to promote their absorption into fat, liver, and skeletal muscle cells. It also suppresses the breakdown of proteins into amino acids. Circulating insulin levels stimulate cellular glucose oxidation, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and proteogenesis to maintain glucose […]
Salivary Interleukin-8
Interleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as neutrophil chemotactic factor, belongs to the CXC chemokine family and mainly serves as an immune mediator of neutrophil-dependent acute inflammation (2). IL-8 is produced in various cells and tissues such as phagocytes and mesenchymal cells exposed to inflammatory stimulus, and primarily targets the recruitment and activation of neutrophil granulocytes and […]
Salivary Estriol
Estriol (1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3,16α,17β-triol; E3) is a female sex steroid hormone largely associated with pregnancy and fetal development. Fetal adrenal DHEA-S is metabolized in the fetal liver to 16α-hydroxy-DHEA-S, which is then converted to estriol in the placenta. (1,2) By the second trimester, about 90% of the estriol produced is derived from this fetal adrenal DHEA-S. (2) […]
Salivary Estradiol
Estradiol is one of the three main estrogenic steroid hormones present in humans. It is the most active naturally secreted estrogen. (1) In menstruating women, estradiol is produced primarily by the ovarian follicles from testosterone, with additional amounts produced by extraglandular conversion of testosterone in peripheral tissues. (1,2,3,4) Concentrations peak mid-cycle, marking ovulation, followed by […]
Salivary DHEA-S
DHEA-S is a steroid hormone produced primarily in the adrenal cortex. It is the sulfated version of the human steroid DHEA, and, like DHEA, it is secreted in response to ACTH. DHEA-S has been reported to have a diurnal rhythm, but the findings have varied, and some studies found no variation. (1) DHEA-S in the blood […]
Salivary DHEA
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a steroid hormone produced principally in the adrenal cortex. In men, it is estimated that 10-25% of the circulating DHEA is secreted by the testes. (1) DHEA and its sulfated analog DHEA-S serve primarily as precursors that circulate to peripheral tissues, where they are converted to androgens and estrogens. (1,2) This allows […]
Salivary Cytokine Panel
The expanded Salimetrics Cytokine Panel provides researchers the flexibility to measure 4 core cytokine (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 & TNF-α) levels in saliva samples – plus, up to 8 additional cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-5, IL-7, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, and IL-17A). Researchers now have the capacity to customize a panel that fits their research question. Salivary cytokine […]
Salivary Cotinine
When nicotine from tobacco smoke is taken into the lungs and enters the bloodstream, the principle metabolite produced in the liver is cotinine. Cotinine diffuses easily from blood into saliva, and salivary cotinine and blood levels are highly correlated. (1) Cotinine in saliva has a longer half-life than nicotine (more than 10 hours), and the […]
Salivary Alpha-Amylase
Alpha-Amylase (or α-Amylase) is a digestive enzyme that hydrolyses alpha-1,4 bonds of large polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen, yielding the smaller by-products of glucose and maltose. (1) Alpha amylase is synthesized in the acinar cells of the saliva glands and stored in secretory granules inside these cells. (2) Its release from the salivary cells […]
Salivary Aldosterone
Recent studies have shown that primary aldosteronism (PA) is the most common cause of secondary hypertension with a prevalence of approximately 5-10% among all hypertensive patients and an even higher prevalence among selected patients with advanced stages of hypertension and resistant hypertension. (1) Screening for PA among hypertensive patients is important due to its association with risk […]
Salivary Cortisol
Cortisol (hydrocortisone, Compound F) is the major glucocorticosteroid hormone produced in the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is actively involved in the regulation of calcium absorption, blood pressure maintenance, anti-inflammatory function, gluconeogenesis, gastric acid, pepsin secretion, and immune function. (1,2,3) Cortisol production has a circadian rhythm. (4) Levels peak in the early morning and drop to the […]
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)