IL-6 and TNF-α are critical pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the regulation of immune responses and inflammation. IL-6 functions as both a pro- and anti-inflammatory mediator and is particularly relevant in studies of metabolic dysregulation, insulin resistance, and obesity. TNF-α is implicated in the pathogenesis of a wide range of inflammatory conditions, including insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, due to its potent role in inducing systemic inflammation.
IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that plays a key regulatory role in suppressing excessive immune responses and mitigating tissue damage. It counteracts the effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α, making it an important marker for immune regulation and homeostasis in chronic inflammatory conditions.
The Salimetrics Core Lab is supported by the latest advancements in DBS analysis, as demonstrated in published research, including the work of Thomas McDade, Ph.D., who also serves as a scientific advisor for DBS studies. This ensures that Salimetrics’ methodologies align with the expected performance standards established by experts in the field.
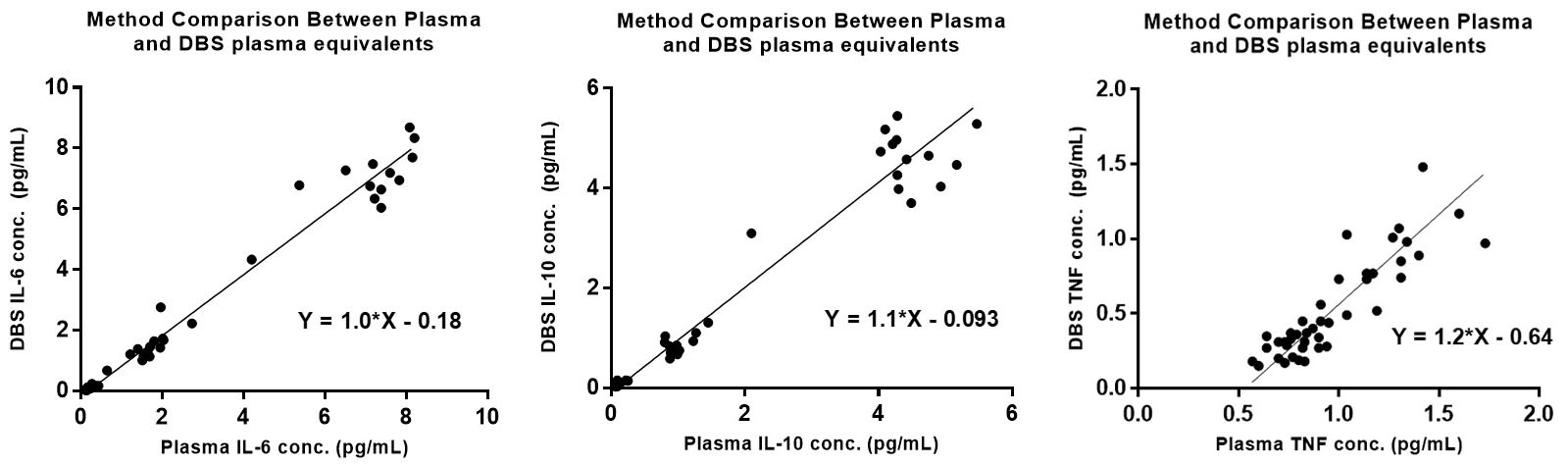
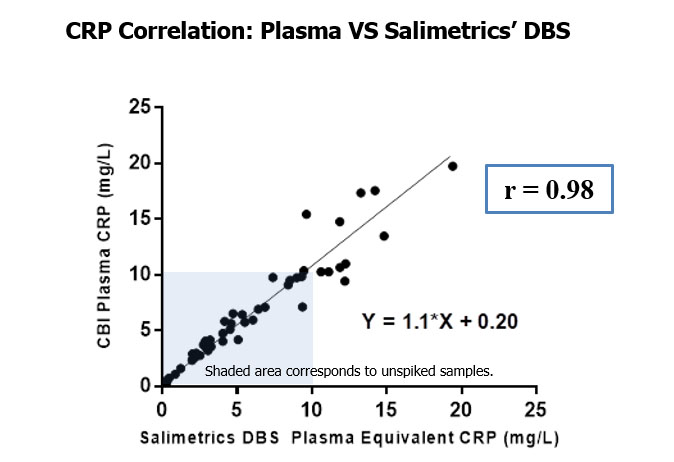
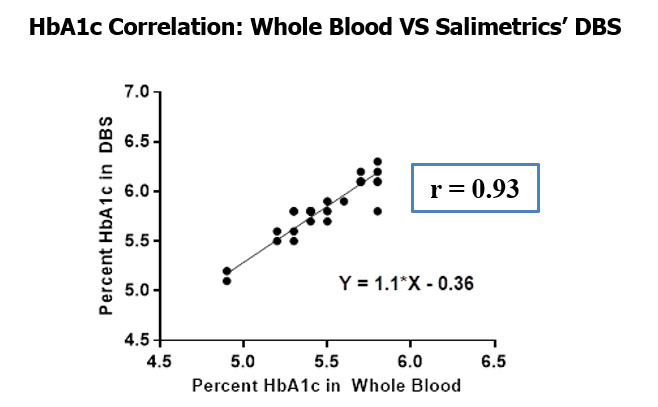
Figure 1. Method comparison between matched samples of whole blood DBS and plasma. The solid line indicates the Deming regression fit with Spearman correlations of r = 0.97 (IL-6), r = 0.92 (IL-10), and r = 0.86 (TNF-alpha).
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)