Need Help?
Ask an expert
1. How to collect Salivary SIgA
APPROVED SALIVARY SECRETORY IgA COLLECTION METHODS
Salivary SIgA Collection Protocol
Collection volume, general considerations, and basic guidelines to maximize salivary SIgA sample integrity. Use this analyte-specific collection protocol to plan you collection methodology and sampling schemes.

2. How to Assay for Salivary SIgA
Send Saliva Samples to Salimetrics
Add to StudyEasy and accurate results from the Salimetrics CoreLab+ Laboratory.
Order Code5180
Salivary Secretory IgA ELISA Kit
Add to Study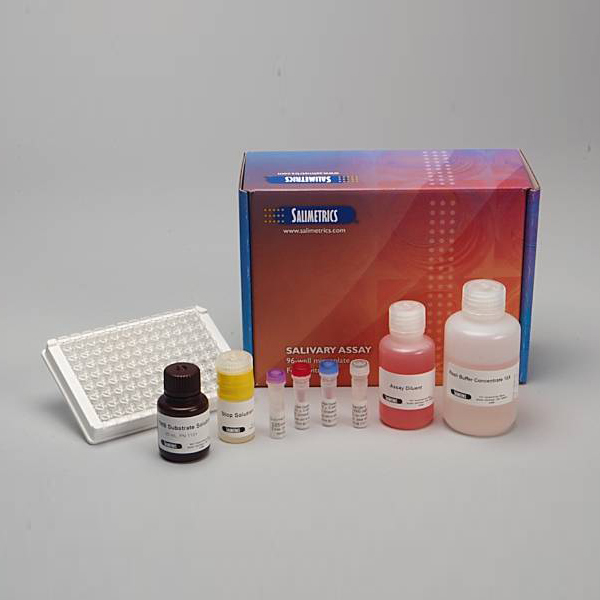
Salimetrics Assay #1-1602
The Salimetrics Salivary Secretory IgA (SIgA, Secretory Immunoglobulin-A) Enzyme Immunoassay Kit was specifically designed to standardize the detection of secretory IgA in saliva samples for research and biomedical laboratories. Using a small sample volume, this assay kit has an extended range which spans the expected secretory IgA levels found in human saliva. The average inter- and intra-assay precision coefficients of variation are low with no deleterious matrix effects often found in saliva which are characterized through dilution- and spike-recovery validation procedures. This secretory IgA assay kit has also been formatted to minimize cross reactivity for related cytokines. Read More...| Assay Protocol |
|---|
| Rev. 09.20.24
|
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Catalog#: | 1-1602 |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO |
| Format: | 96-well plate |
| Assay Time: | ~ 4 hrs |
| Sample Volume/Test: | 25 µL |
| Sensitivity: | 2.5 µg/mL |
| Assay Range: | 2.50 µg/mL – 600 µg/mL |
| Storage Requirements: | 2-8°C |
| Tests Per Kit | |
|---|---|
| Singlet: | 76 |
| Duplicate: | 38 |
| Target Analyte |
|---|
Technical Documentation
Assay Kit Overview
Intended Use
The Salimetrics SIgA Indirect Enzyme Immunoassay Kit is a competitive immunoassay specifically designed and validated for the quantitative measurement of salivary SIgA. It is not intended for diagnostic use. This assay kit was designed and optimized for salivary research use in humans. Salimetrics has not validated this kit for serum, plasma or saliva samples from any other species.
Introduction
Secretory Immunoglobulin A (SIgA) is the dominant immunoglobulin in external secretions that bathe mucosal surfaces (respiratory, intestinal, and reproductive), where it acts as a key component of the immune system’s “first line of defense” against microbial invasion. Dimeric IgA secreted by mucosal plasma cells adjacent to the salivary glands is bound and transported through the salivary cells by a polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR). The IgA dimer, in complex with a fragment of the pIgR polypeptide, is then released into saliva as secretory IgA (SIgA). IgA-producing plasma cells are generally undetectable in the mucosae before 10 days of age, but they increase rapidly thereafter. SIgA levels are generally thought to be very low in newborn infants and to rise quickly during the first month of life. Levels of salivary SIgA continue to increase as children age, stabilizing within the adult range around 5-7 years. Reports of changes in SIgA secretion in old age are inconsistent, with both increases and decreases having been observed. Relative numbers of IgA-producing plasma cells are higher in the submandibular and sublingual glands compared to the parotid glands, and even higher in certain minor glands, leading to differing levels of SIgA in the secretions from these glands. It is speculated that greater density of plasma cells in certain glands may be due to increased antigenic interactions in those parts of the mouth. The active transport mechanism into saliva for SIgA serves as a rate-limiting factor, and salivary levels of SIgA decrease as flow rates increase. The contributions to whole saliva from the various salivary glands in the mouth also vary greatly according to the rate of flow. The literature therefore recommends that variability in salivary flow rate should be taken into account when estimating salivary levels of SIgA and making comparisons between individuals. Salivary SIgA levels vary in a complex fashion in response to stress, mood, and emotionality. The present enzyme immunoassay protocol represents a significant advance over the traditional SIgA measurement approach to employing single radial immunodiffusion (SRID). This enzyme immunoassay is designed to capture the full range of salivary SIgA levels and uses only 25 μL of saliva per test, with minimal incubation times.
Salivary Secretory IgA Assay Principle
This is an indirect competitive immunoassay kit. A constant amount of goat anti-human SIgA conjugated to horseradish peroxidase is added to tubes containing specific dilutions of standards or saliva. The antibody enzyme conjugate binds to the SIgA in the standard or saliva samples. The amount of free antibody enzyme conjugate remaining is inversely proportional to the amount of SIgA present in the sample. After incubation and mixing, an equal solution from each tube is added in duplicate to the microtitre plate coated with human SIgA. The free or unbound antibody enzyme conjugate binds to the SIgA on the plate. After incubation, unbound components are washed away. Bound SIgA Antibody Enzyme Conjugate is measured by the reaction of the horseradish peroxidase enzyme to the substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). This reaction produces a blue color. A yellow color is formed after stopping the reaction with an acidic solution. The optical density is read on a standard plate reader at 450 nm. The amount of SIgA Antibody Enzyme Conjugate detected is inversely proportional to the amount of SIgA present in the sample.
3. Technical Summary
| Analyte Summary | |
|---|---|
| Analyte: | Secretory Immunoglobulin A |
| Aliases: | SIgA, Secretory IgA |
| Serum-Saliva Correlation: | NA |
| *Optimum Collection Volume: | 50 μL |
| Special Considerations |
|---|
| SIgA is Location Dependent SIgA is Flow Rate Dependent (μg/mL) Passive Drool is the Recommended Collection Method |
| Assay Summary | |
|---|---|
| Methodology: | ELISA |
| Sensitivity: | 2.5 μg/mL |
| Assay Range: | 2.50 µg/mL – 600 µg/mL |
| Assay Type: | Quantitative |
Background
Secretory Immunoglobulin A (SIgA) is a subclass of Immunoglobulin A (IgA), an antibody that plays a critical role in mucosal immunity. SIgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions from tear glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, the respiratory system, the genito-urinary tract, and the gastrointestinal tract. (1) SIgA is not synthesized by mucosal epithelial cells in these structures or derived from blood. Instead, it is produced by B-lymphocytes adjacent to the mucosal cells, then transported through the cell interiors, and released into the secretions from the cells. (2) SIgA plays a key role in protecting vulnerable areas such as the oral cavity, lungs, and gut from invading pathogens. (1) Differences in SIgA levels in the saliva from different glands have been observed in humans, with the highest levels found in the minor saliva glands. (2,3) SIgA exhibits a diurnal rhythm, decreasing from the highest levels in the morning to the lowest in the evening. (4) Levels of SIgA in saliva vary in response to physical and psychological stress through interactions with the autonomic nervous system. (5,6) SIgA levels in saliva are affected by flow rates, with concentrations normally decreasing as flow rates increase. Measurement of flow rates is advisable in order to express SIgA secretion as a function of time. (6)
References & Salivary Secretory IgA Research
- Holmgren, J., Czerkinsky, C. (2005). Mucosal immunity and vaccines. Nature Medicine, 11(4 Suppl), s45-53.
- Brandtzaeg, P. (2007). Do salivary antibodies reliably reflect both mucosal and systemic immunity? Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1098, 288-311.
- Crawford, J.M., Taubman, M.A., Smith D.J. (1975). Minor salivary glands as a major source of secretory immunoglobulin A in the human oral cavity. Science, 190(4220), 1206-9.
- Li, T.-L., Gleeson, M. (2004). The effect of single and repeated bouts of prolonged cycling and circadian variation on saliva flow rate, immunoglobulin A and alpha-amylase responses. J Sports Sci, 22(11-12), 1015-1024.
- Tsujita, S., Morimoto, K. (1999). Secretory IgA in saliva can be a useful stress marker. Env Health Prev Med, 4, 1-8.
- Bishop, N.C., Gleeson, M. (2009). Acute and chronic effects of exercise on markers of mucosal immunity. Front Biosci, 1(14), 4444-56.
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)