Need Help?
Ask an expert
1. How to collect Salivary IgM
Salivary IgM Collection Protocol
Collection volume, general considerations, and basic guidelines to maximize salivary IgM sample integrity. Use this analyte-specific collection protocol to plan you collection methodology and sampling schemes.

2. How to Assay for Salivary IgM
Send Saliva Samples to Salimetrics
Add to StudyEasy and accurate results from the Salimetrics CoreLab+ Laboratory.
Order Code5176
Salivary IgM ELISA Kit
Add to Study
Salimetrics Assay #1-4002
The Salimetrics Salivary Total Human IgM (ImmunoglobulinM) Enzyme Immunoassay Kit was specifically designed to quantify levels of total human IgM in saliva samples and other oral fluids , which can be used for sample quality assurance and as inclusion criteria when using oral fluid as an alternative sample type for serological studies. Pathogen specific IgM is indicative of recent acute exposure, and when used together with total IgM, researchers can confidently track outbreak scenarios and minimize false negatives due to inadequate total IgM levels while using the convenience of oral fluid sampling. Read More...| Assay Protocol |
|---|
| Rev. 11.12.21
|
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Catalog#: | 1-4002 |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO |
| Format: | 96-well plate |
| Assay Time: | ~ 3 hrs |
| Sample Volume/Test: | 10 µL |
| Sensitivity: | 0.03 ng/mL |
| Assay Range: | 0.39 – 25 ng/mL |
| Storage Requirements: | 2-8°C |
| Tests Per Kit | |
|---|---|
| Singlet: | 76 |
| Duplicate: | 38 |
| Target Analyte |
|---|
Technical Documentation
Assay Kit Overview
Intended Use
The Salimetrics® Salivary Human Total IgM ELISA Kit is an enzyme-linked immunoassay specifically designed and validated for the quantitative measurement of human total IgM in oral fluid. It is not intended for diagnostic use. This assay kit was optimized for human salivary research and has not been validated for other human sample types, such as serum or plasma or samples from other species. For further information about this kit, its application, or the procedures in this insert, please contact the technical service team at Salimetrics or your local sales representative.
Introduction
Immunoglobulin M, or IgM, is one of five classes of antibodies found in humans, and is present as part of both the natural and adaptive immune response. Natural IgMs are low affinity pentameric molecules that bind to invading pathogens without requiring prior exposure. They act to directly neutralize viruses, activate complement, trigger phagocytosis and drive antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity. Adaptive IgM is the first antibody produced in response to invading pathogens and functions in a similar way to natural IgM, but are higher affinity molecules and are an important part of the adaptive immune response (4). IgM is the first immunoglobulin molecule found in the fetus, developing in the second half of pregnancy. The majority of IgM is pentameric and includes a molecule referred to as the J chain, a key structural component also found in polymeric IgA. IgM also forms tetramers and hexamers, however in this case the J chain is absent. In contrast to IgG, IgM antibodies peak early in the course of humoral immune responses waning after several weeks and are thus useful in the determination of recent infections or pathogen exposure. One important use for measuring antigen specific IgM in saliva is during serological surveys when assessing outbreaks of infectious diseases, for instance with the recent COVID-19 outbreak. Similar to IgM, the major source of IgM in saliva is blood, and its entry is through gingival crevicular fluid (GCF). Due to this, the total amount of IgM can vary depending on the level of serum component representation. Therefore, when measuring pathogen specific IgM, total IgM can be used to qualify a saliva sample to assure sufficient levels of total IgM in the saliva sample and provide confidence in the pathogen specific IgM results. In this regard, total IgM may be essential to prove a negative pathogen specific test result. In addition, this assay may be used to qualify samples for testing after sample storage.
SALIVARY HUMAN TOTAL IgM ASSAY PRINCIPLE
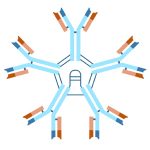
This is an indirect sandwich ELISA kit. A “sandwich” is formed when the pre-coated capture Anti-Human IgM antibody present on the plate binds IgM in standards & samples, which is then bound by the Anti-Human IgM detection antibody linked to horseradish peroxidase. After each incubation, unbound components are washed away. Bound Anti-Human IgM Antibody Enzyme Conjugate is then added and the levels measured by the reaction of the horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzyme to the substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). This reaction produces a blue color. A yellow color is formed after stopping the reaction with an acidic solution. The optical density is read on a standard plate reader at 450 nm. The total amount of IgM Antibody Enzyme Conjugate detected is directly proportional to the amount of Total Human IgM present in the sample.
3. Technical Summary
| Analyte Summary | |
|---|---|
| Analyte: | Total Immunoglobulin M |
| Aliases: | IgM |
| Serum-Saliva Correlation: | NA |
| *Optimum Collection Volume: | 50 μL |
| Assay Summary | |
|---|---|
| Methodology: | ELISA |
| Sensitivity: | 0.03 ng/mL |
| Assay Range: | 0.39 – 25 ng/mL |
| Assay Type: | Quantitative |
Background
Immunoglobulin M, or IgM, is present in two major forms in the circulation referred to as natural or adaptive (1). Natural IgMs are low affinity pentameric molecules that bind to invading pathogens without requiring prior exposure (2). They act to directly neutralize viruses, activate complement, trigger phagocytosis and drive antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (3). Adaptive IgM is the first antibody produced in response to invading pathogens and functions in a similar way to natural IgM but are high affinity molecules and are an important part of an adaptive immune response (4). The majority of IgM is pentameric and includes a molecule referred to as the J chain, which is also a key structural component found in polymeric IgA. IgM also naturally forms hexamers, however in this case the J chain is absent. In contrast to IgG, IgM antibodies peak early in the time course of humoral immune responses waning after several weeks and are thus useful in the diagnosis of recent infections or pathogen exposure. One important use for measuring antigen specific IgM in saliva is during serological surveys when assessing outbreaks of infectious diseases, for instance with the recent COVID-19 outbreak (4). Similar to IgG, since the major salivary source of IgM is blood plasma, the total amount of IgM varies over time depending on how much serum components are introduced into oral fluid and is subject to the influences of dilution by salivary flow. Therefore, when measuring pathogen specific IgM, total IgM can be used to qualify a saliva sample to assure sufficient levels of total IgM to provide confidence in pathogen specific IgM results. In this regard, total IgM may be essential to prove a negative pathogen specific test result. In addition, this assay may be used to qualify samples for testing after sample storage.
References & Salivary IgM Research
- Fereidan-Esfahani M, Nayfeh T, Warrington A, Howe CL, Rodriguez M. IgM Natural Autoantibodies in Physiology and the Treatment of Disease. Methods in molecular biology. 2019;1904:53-81.
- Michaud E, Mastrandrea C, Rochereau N, Paul S. Human Secretory IgM: An Elusive Player in Mucosal Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2020;41(2):141-56.
- Madar R, Straka S, Baska T. Detection of antibodies in saliva–an effective auxiliary method in surveillance of infectious diseases. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2002;103(1):38-41.
- Brandtzaeg P. Do salivary antibodies reliably reflect both mucosal and systemic immunity? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2007;1098:288-311.
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)