Need Help?
Ask an expert
1. How to collect Salivary Cortisol
APPROVED SALIVARY CORTISOL COLLECTION METHODS
Salivary Cortisol Collection Protocol
Collection volume, general considerations, and basic guidelines to maximize salivary cortisol sample integrity. Use this analyte-specific collection protocol to plan you collection methodology and sampling schemes.

2. How to Assay for Salivary Cortisol
Send Saliva Samples to Salimetrics
Add to StudyEasy and accurate results from the Salimetrics CoreLab+ Laboratory.
Order Code5100
Salivary Cortisol ELISA Kit
Add to Study
Salimetrics Assay #1-3002
Using a small sample volume, this assay kit has an extended range that spans the expected cortisol levels found in human saliva. The average inter- and intra-assay precision coefficients of variation are low with no deleterious matrix effects often found in saliva which are characterized through dilution- and spike-recovery validation procedures. The Salimetrics cortisol assay kit has also been formatted to minimize cross reactivity for related steroids. Salimetrics salivary assay kits are expertly designed, developed and validated to ensure accuracy in saliva and proven to deliver precision results for biomarkers in saliva. Read More...| Assay Protocol |
|---|
| Rev. 04.01.25 (1-3002)
|
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Catalog#: | 1-3002 |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO |
| Format: | 96-well plate |
| Assay Time: | ~ 2 hrs |
| Sample Volume/Test: | 25 µL |
| Sensitivity: | <0.007 ug/dL |
| Assay Range: | 0.012-3.000 ug/dL |
| Storage Requirements: | 2-8°C |
| Tests Per Kit | |
|---|---|
| Singlet: | 78 |
| Duplicate: | 39 |
| Target Analyte |
|---|
Technical Documentation
Assay Kit Overview
Intended Use
The Salimetrics® Cortisol Enzyme Immunoassay Kit is a competitive immunoassay specifically designed and validated for the quantitative measurement of salivary cortisol. It is not intended for diagnostic use. It is intended only for research use in humans and some animals. Salimetrics has not validated this kit for serum or plasma samples.
Introduction
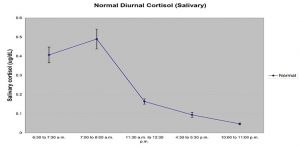
Cortisol (hydrocortisone, Compound F) is the major glucocorticoid produced in the adrenal cortex. Cortisol production has a circadian rhythm, with levels peaking in the early morning and dropping to lowest values at night. Levels rise independently of circadian rhythm in response to stress.
In blood, only about 5-10% of cortisol is in its unbound or biologically active form. The remaining cortisol is bound to serum proteins. Unbound serum cortisol enters saliva via intracellular mechanisms; in saliva, the majority of cortisol remains unbound to protein. Salivary cortisol levels are unaffected by salivary flow rate and are relatively resistant to degradation from enzymes or freeze-thaw cycles. Studies consistently report high correlations between serum and salivary cortisol, indicating that salivary cortisol levels reliably estimate serum cortisol levels.
Cortisol Assay Principle
This is a competitive immunoassay kit. Cortisol in standards and samples compete with cortisol conjugated to horseradish peroxidase for the antibody binding sites on a microtitre plate. After incubation, unbound components are washed away. Bound cortisol enzyme conjugate is measured by the reaction of the horseradish peroxidase enzyme to the substrate tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). This reaction produces a blue color. A yellow color is formed after stopping the reaction with an acidic solution. The optical density is read on a standard plate reader at 450 nm. The amount of cortisol enzyme conjugate detected is inversely proportional to the amount of cortisol present, in the sample.
Diagnostic Salivary Cortisol ELISA Kit (FDA, CE Mark)
Add to Study
Salimetrics Assay #1-3102 (in vitro diagnostic use)
Using a small sample volume, this assay kit has an extended range that spans the expected cortisol levels found in human saliva. The average inter- and intra-assay precision coefficients of variation are low with no deleterious matrix effects often found in saliva which are characterized through dilution- and spike-recovery validation procedures. The Salimetrics cortisol assay kit has also been formatted to minimize cross reactivity for related steroids. Salimetrics salivary assay kits are expertly designed, developed and validated to ensure accuracy in saliva and proven to deliver precision results for biomarkers in saliva. Read More...| Assay Protocol |
|---|
| Rev. 09.06.24 (1-3102)
|
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Catalog#: | 1-3102 |
| Regulatory Status: | 510(k), CE Mark |
| Format: | 96-well plate |
| Assay Time: | ~ 2 hrs |
| Sample Volume/Test: | 25 µL |
| Sensitivity: | <0.007 ug/dL |
| Assay Range: | 0.012-3.000 ug/dL |
| Storage Requirements: | 2-8°C |
| Tests Per Kit | |
|---|---|
| Singlet: | 78 |
| Duplicate: | 39 |
| Target Analyte |
|---|
Technical Documentation
3. Technical Summary
| Analyte Summary | |
|---|---|
| Analyte: | Cortisol |
| Aliases: | hydrocortisone, Compound F |
| Serum-Saliva Correlation: | 0.91 |
| *Optimum Collection Volume: | 75 μL |
| Interfering Factors |
|---|
| Bovine hormones normally present in dairy products can cross-react with anti-cortisol antibodies and cause false results. Hormone based oral contraceptives and estrogens can cause temporary increase in CBG, potentially lowering cortisol levels in saliva. Multiple medications mimic the structure of cortisol and have the potential to influence cortisol levels in saliva. |
| Assay Summary | |
|---|---|
| Methodology: | ELISA |
| Sensitivity: | <0.007 ug/dL |
| Assay Range: | 0.012-3.000 ug/dL |
| Assay Type: | Quantitative |
| *Salivary Cortisol Example Ranges | ||
|---|---|---|
| Group | Number | Overall Range (ug/dL) |
| Children, neonatal | 275 | ND - 3.417 |
| Children, age 6 months | 165 | ND - 2.734 |
| Group | Number | Overall Range (ug/dL) |
| Normal subjects | 19 | 0.007 - 0.115 |
| Cushing's subjects | 21 | 0.130-2.972 |
Background
Cortisol (hydrocortisone, Compound F) is the major glucocorticosteroid hormone produced in the adrenal cortex. Cortisol is actively involved in the regulation of calcium absorption, blood pressure maintenance, anti-inflammatory function, gluconeogenesis, gastric acid, pepsin secretion, and immune function. (1,2,3) Cortisol production has a circadian rhythm. (4) Levels peak in the early morning and drop to the lowest concentration at night. (5) Levels rise independently of circadian rhythm in response to stress. (6) Increased cortisol production is associated with Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal tumors, while decreased cortisol production is associated with adrenal insufficiency (e.g., Addison’s disease) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency. (7) In the blood only 1 to 15% of cortisol is in its unbound or biologically active form. The remaining cortisol is bound to serum proteins. (8) Unbound serum cortisol enters the saliva via intracellular mechanisms, and in saliva the majority of cortisol remains unbound to protein. (9) Salivary cortisol levels are unaffected by salivary flow rate or salivary enzymes. (10) Studies consistently report high correlations between serum and saliva cortisol, indicating that salivary cortisol levels reliably estimate serum cortisol levels. (11,12,13)
References & Salivary Cortisol Research
-
- Migeon, C.J., & Lanes, R.L. (1990). Adrenal cortex: hypo- and hyperfunction. In F. Lifshitz (ed.), Pediatric endocrinology, a clinical guide (2nd ed.), (pp. 333-52). New York: Marcel Dekker.
- Drucker, S., New, M.I. (1987). Disorders of adrenal steroidogenesis. Pediatr Clin North Am, 34(4), 1055-66.
- Fischbach, F.T. (1992). The manual of laboratory and diagnostic tests, (4th ed.). Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott.
- Dorn, L.D., Lucke, J.F., Loucks, T.L., Berga, S.L. (2007). Salivary cortisol reflects serum cortisol: analysis of circadian profiles. Ann Clin Biochem, 44(pt 3), 281-84.
- Chernow, B., Alexander, H.R., Smallridge, R.C., et al. (1987). Hormonal responses to graded surgical stress. Arch Intern Med, 147(7), 1273-78.
- Kreiger, D.T. (1975). Rhythms of ACTH and corticosteroid secretion in health and disease and their experimental modification. J Steroid Biochem, 6(5), 758-91.
- Rothfield, B. (1974). Plasma cortisol. In: B. Rothfield (ed.), Nuclear medicine–in vitro (pp. 120-5). Philadelphia: Lippincott.
- Robin, P., Predine, J., Milgrom, E. (1977). Assay of unbound cortisol in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 46(2), 277-83.
- Vining, R.F., McGinley, R.A., Symons, R.G. (1983). Hormones in saliva: mode of entry and consequent implications for clinical interpretation. Clin Chem, 29(10), 1752-56.
- Vining, R.F., McGinley, R.A. (1987). The measurement of hormones in saliva: Possibilities and pitfalls. J Steroid Biochem, 27(1-3), 81-94.
- Francis, S.J., Walker, R.F., Riad-Fahmy, D., et al. (1987). Assessment of adrenocortical activity in term newborn infants using salivary cortisol determinations. J of Pediatrics, 111, 129-33.
- Hiramatsu, R. (1981). Direct assay of cortisol in human saliva by solid phase radioimmunoassay and its clinical applications. Clinica Chimica Acta, 117, 239-249.
- Vining, R.F., McGinley, R.A., Maksvytis, J.J., Ho, K.Y. (1983). Salivary cortisol: A better measure of adrenal cortical function than serum cortisol. Ann Clin Biochem, 20(pt 6), 329-35.
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)