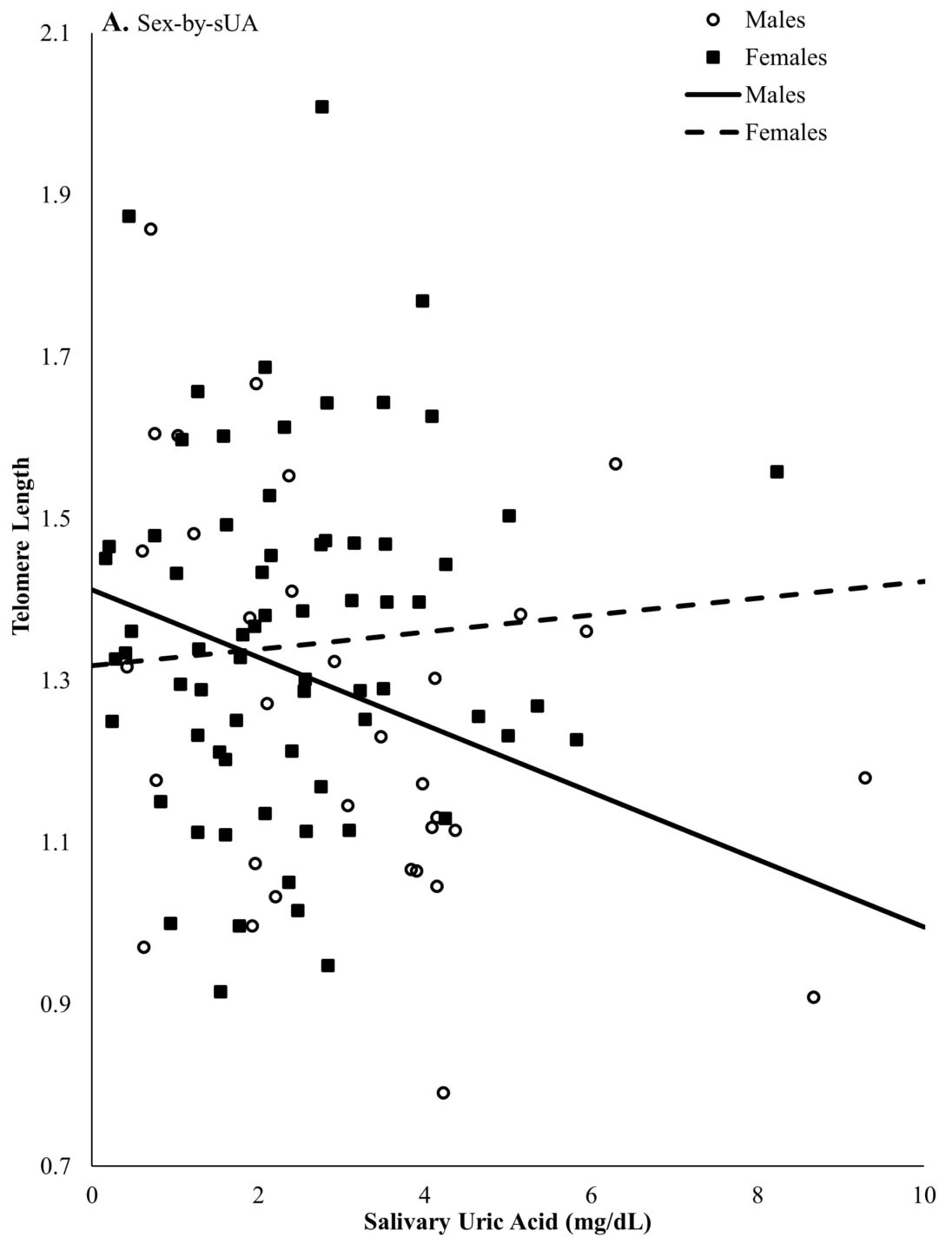
“We examined how salivary uric acid relates to telomere length among African Americans, considering age and gender through an intersectional lens. Our findings reveal that uric acid is associated with shorter telomeres particularly among younger adults and men, with different mechanisms operating across intersectional identities—biological vulnerability in men versus social moderation in women. This research demonstrates that intersectionality operates through multiple pathways simultaneously and suggests that targeted interventions addressing both biological and social factors may be needed to mitigate cellular aging and health disparities in African American communities.” – Stefan Goetz, PhD
Salivary Uric Acid, Telomere Length, and Intersectionality in African Americans
Age and Gender Intersectionality Among African Americans: Salivary Uric Acid is Associated with Shorter Telomere Length in Younger Adults and Men
Goetz, S. M. M., Lucas, T., Finegood, E., Lin, J., & Granger, D. (2025). Psychoneuroendocrinology
Research Highlights: Research Highlight: This publication reports that higher salivary uric acid is linked to shorter telomeres, a marker of accelerated cellular aging, among younger African Americans and men. The study also highlights how age, gender, and experiences of discrimination shape biological stress pathways. Findings suggest uric acid may play a role in age-related diseases and contribute to health disparities.
Research Highlights: Research Highlight: This publication reports that higher salivary uric acid is linked to shorter telomeres, a marker of accelerated cellular aging, among younger African Americans and men. The study also highlights how age, gender, and experiences of discrimination shape biological stress pathways. Findings suggest uric acid may play a role in age-related diseases and contribute to health disparities.

Keywords: Uric acid, saliva, telomere length, cellular aging, health disparities, African American communities.
*Note: Salimetrics provides this information for research use only (RUO). Information is not provided to promote off-label use of medical devices. Please consult the full-text article.
 Contact: Salimetrics (USA)
Contact: Salimetrics (USA)